Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA3643
Pages:98
Published On:September 2025
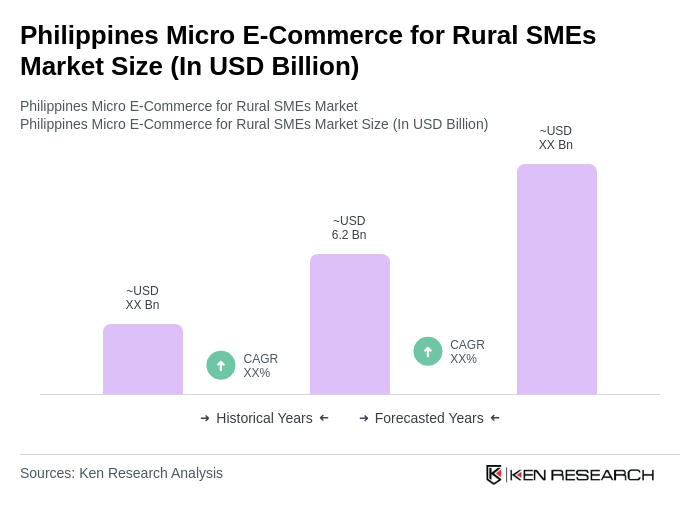
By Type:The market is segmented into various types, including Food and Beverages, Handicrafts and Local Artifacts, Clothing and Accessories, Home and Living Products, Health and Beauty Products, Electronics and Gadgets, Agricultural Inputs and Produce, Digital Services, and Others. Each sub-segment caters to specific consumer needs and preferences, contributing to the overall market growth. Local homegrown brands and niche products are gaining significant traction, particularly those using local ingredients and reflecting Filipino culture, with specialty categories like eco-friendly products, organic produce, and artisanal goods experiencing increased popularity among socially conscious consumers.
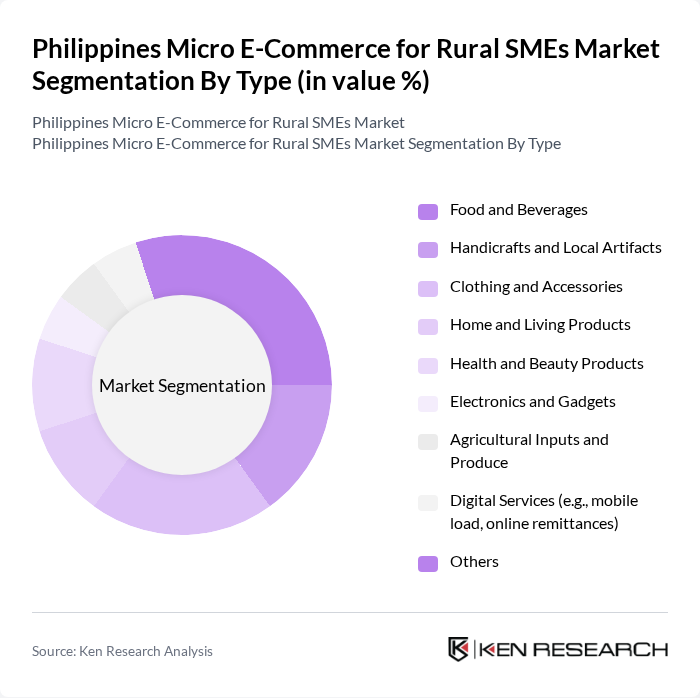
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Individual Consumers, Small Businesses and Micro-Entrepreneurs, Cooperatives and Community Groups, Non-Governmental Organizations, and Government Agencies. Each group has distinct purchasing behaviors and requirements, influencing the types of products and services offered in the market. The entrepreneurial culture in the Philippines has significantly contributed to market development, with home-based entrepreneurs and micro-businesses leveraging digital channels to reach broader audiences, supported by minimal entry costs for establishing online shops on marketplace platforms.
The Philippines Micro E-Commerce for Rural SMEs Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Lazada Philippines, Shopee Philippines, Zalora Philippines, GCash, Maya (formerly PayMaya), Globe Telecom, Smart Communications, Foodpanda Philippines, Grab Philippines, Angkas, Kumu, Carousell Philippines, Coins.ph, UnionBank Online, Metrobank Online, TikTok Shop Philippines, GoNegosyo, Cropital, Agrabah Marketplace, Packworks contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of micro e-commerce for rural SMEs in the Philippines appears promising, driven by increasing digital adoption and government initiatives aimed at enhancing connectivity. As more rural entrepreneurs embrace online platforms, the market is likely to witness a surge in innovative business models, particularly in mobile commerce and localized e-commerce solutions. Additionally, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI and data analytics, will further streamline operations and improve customer engagement, fostering sustainable growth in this sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Food and Beverages Handicrafts and Local Artifacts Clothing and Accessories Home and Living Products Health and Beauty Products Electronics and Gadgets Agricultural Inputs and Produce Digital Services (e.g., mobile load, online remittances) Others |
| By End-User | Individual Consumers Small Businesses and Micro-Entrepreneurs Cooperatives and Community Groups Non-Governmental Organizations Government Agencies |
| By Sales Channel | Direct Online Sales (Websites) Social Commerce Platforms (Facebook, TikTok Shop, Instagram) Mobile Applications E-Commerce Marketplaces (Lazada, Shopee, etc.) Community-Based Selling (Viber, Messenger groups) |
| By Distribution Mode | Home Delivery Pick-Up Points Local Market Stalls Third-Party Logistics Providers |
| By Price Range | Low-End Products Mid-Range Products Premium Products |
| By Customer Demographics | Age Groups Income Levels Urban vs Rural Digital Literacy Level |
| By Payment Method | Cash on Delivery Online Banking E-Wallets (GCash, Maya, Coins.ph) Credit/Debit Cards Over-the-Counter Payments |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Rural SME E-commerce Adoption | 100 | SME Owners, E-commerce Managers |
| Consumer Behavior in Rural E-commerce | 90 | Rural Consumers, Community Leaders |
| Logistics and Delivery Challenges | 60 | Logistics Providers, Delivery Personnel |
| Payment Systems Utilization | 50 | Finance Managers, Payment Gateway Representatives |
| Marketing Strategies for Rural SMEs | 40 | Marketing Managers, Business Development Officers |
The Philippines Micro E-Commerce for Rural SMEs Market is valued at approximately USD 6.2 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by increased internet penetration and mobile device usage among rural consumers.